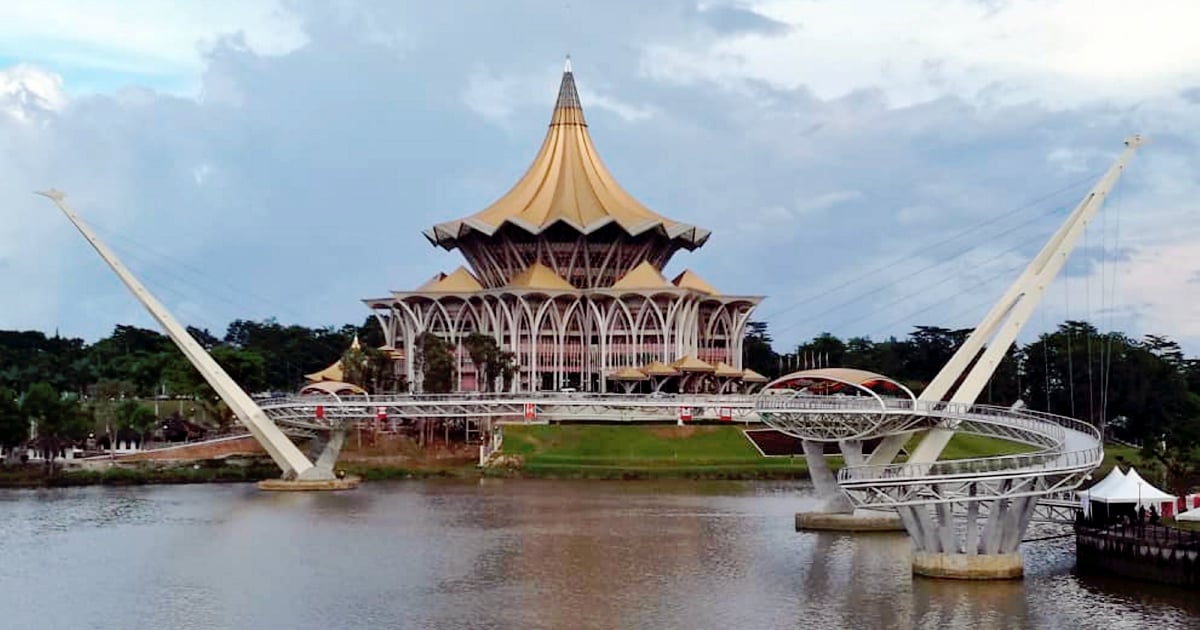
Example Sarawak Local Authority
C A District Council named in part III of the First Schedule.
Example sarawak local authority. Introduction In Sarawak the local authorit ies LA are part of the constitutional structure of the State Government and they are confined with the authority as prescribed in the Local Authorities Ordinance 1996. A particular Local Authority can make a law to suit local needs and that Local Authority will have the knowledge of what is best for the locality rather than Parliament. 1 Erection of compartments galleries lofts etc in buildings 3 Local authority may remove 18.
Established under the Local Authorities Ordinance 1996. MPKS 2016 Padawan Municipal Council. Sarawak LawNet LOCAL AUTHORITIES 3 Section 38.
Established on July 8 1978 to serve as the government agency to take charge of physical planning and development in Bintulu. BDA was formed following the. Sarawak State Secretary Office Level 20 Wisma Bapa Malaysia.
Ministry of Education Science and Technological Research Sarawak. 98 local authorities in the Peninsular Malaysia are planning authorities. Local Authority Fund and Local Treasury 41.
The Local Authorities Ordinance 1996 had come into force on January 1998 and was intended to consolidate the laws on local authorities and to repeal the previous Local Authority. B A Municipal Council named in part II of the first Schedule. Famed for its caves and karst ecosystems Gunung Mulu National Park in Malaysian Borneos Sarawak state is a UNESCO World Heritage Site home to more than 81 mammal species 270 varieties of.
1 Trees not to be planted within 4 metres of street. Municipal Council Majlis Perbandaran examples. Hedges and trees bordering streets to be trimmed 20.
A The local authority or statutory body is given the authority by any written law for the appropriate benefits or have connection with the implementation of regulatory functions and enforcement. Transferability of local authority staff PART V GENERAL FINANCIAL PROVISIONS 39. Petra Jaya 93502 Kuching.
District Council Majlis Daerah example. Other laws regulating the running of local authorities in Sarawak. Local authority revenue 40.
Besides that Delegated Legislation can be used to cover a situation that Parliament had not anticipated at the time it enacted the piece of legislation which makes it flexible and very useful to law-making. And b The supply made by the local authority or statutory body is not the. City HallCity Council Dewan Bandaraya Majlis Bandaraya examples.
Hurry sign up now to enjoy the benefits. BDA 1978 Kota Samarahan Municipal Council Majlis Perbandaran Kota Samarahan. Local authorities in the states of Sabah and Sarawak are governed by their Ordinances that mandate the state governments as the planning authority hence they do not fall under the purview of Ministry of Urban Wellbeing Housing and Local Government of.
Ministry of Urban Development and Natural Resource Level 9 Wisma Sumber Alam Stadium Road Petra Jaya 93050 Kuching Sarawak Malaysia. Loans by Government 44. In Sarawak local authorities were established under the Local Authority Ordinance 1996.
Borrowing powers for special purposes 43. Bintulu Development Authority BDA has also included in the above-mentioned sub-section b. Majlis Bandaraya Kuching Selatan MBKS Also known as the South Kuching Municipal Council in English.
1 Removal of roofs and walls made of combustible materials 2 Renewal or repairing with combustible materials 17. Local Government Ordinance 1961 Sarawak No11 of 1996 - Local Government in Sarawak Local Authorit means - a A city Administration named in Part I of the First Schedule. Advances by way of overdraft 45.
This ordinance is the successor of pre-independence law the Local Government Ordinance 1948. THE local authorities in Sarawak have to date completed 290 infrastructure projects while 179 more are at various stages of implementation says Local. MPP 1996 Sibu Municipal Council.
Level 4 Plaza Aurora Jalan McDougall 93000 Kuching Sarawak.